双组分信号转导系统(two component signal transduction system,TCS)广泛存在于原核生物,多由组氨酸激酶(histidine kinase)和反应调节蛋白组成,调控细菌的毒力、环境适应力等[1-4]。然而,肠杆菌科中的荚膜异多糖酸合成调节子(regulator of colanic acid capsule synthesis,Rcs)是一种复杂的TCS,主要含RcsB(反应调节蛋白)、RcsC(组氨酸激酶)、RcsD(磷酸转移蛋白)3个组分。在大肠埃希菌、沙门菌等肠杆菌科细菌中,Rcs可调控细菌抗酸性、毒力等生物学特性[5-11],但其在志贺菌中的调控功能尚未见报道。
志贺菌为胞内寄生菌,其进入人体后需感受宿主细胞内外环境变化而调节相应蛋白的表达以适应所处的微环境。在志贺菌的4个亚群中,福氏志贺菌2a型为我国主要型别[12-14]。本研究拟在福氏志贺菌2a 301株(Shigella flexneri 2a str. 301,Sf301) rcsBDC基因簇生物信息学分析的基础上,分析外环境压力如酸性及高渗条件下Rcs表达情况,为后续探索志贺菌Rcs调控抗环境压力及毒力机制打下基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 实验菌株Sf301由中国医学科学院/北京协和医学院病原生物学研究所病毒基因工程国家重点实验室提供,本实验室保存。
1.1.2 主要试剂胰蛋白胨、酵母提取物购于英国OXIOD公司,氯化钠、盐酸购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司,2×Taq DNA聚合酶、细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒、DNA Marker购于天根生化科技(北京)有限公司,NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-up购于德国MACHEREY-NAGEL公司,RNeasy Mini Kit购于德国Qiagen公司,PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser、SYBR Premix Ex Taq购于日本TaKaRa公司。引物由生工生物(上海)工程技术服务有限公司合成。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 福氏志贺菌rcsBDC基因簇的生物信息学分析自美国国立生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information,NCBI)下载细菌的rcsB、rcsD、rcsC核苷酸序列,菌株包括福氏志贺菌2a 301(NC_004337.2)、其他志贺菌亚群的菌株〔痢疾志贺菌Sd197(NC_007606.1)、鲍氏志贺菌Sb227(CP000036.1)、宋内志贺菌Ss046(CP000038.1)〕,以及肠杆菌科的菌株〔大肠埃希菌UMN026(NC_011751.1)、鼠伤寒沙门菌LT2(NC_003197.2)、伤寒沙门菌CT18(NC_003197.2)、肺炎克雷伯菌MGH 78578(NC_009648.1)、梨火疫病菌ATCC 49946(NC_013971.1)、迟缓爱德华菌FL6-60(NC_017309.1)、鼠疫耶尔森菌CO92(NC_003143.1)、奇异变形杆菌HI4320(NC_010554.1)〕。利用Vector NTI Advance 11-Alignment进行相似性比对,生成进化树。利用SMART数据库对Sf301 RcsB、RcsD、RcsC蛋白的氨基酸序列进行结构域预测(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)。
1.2.2 福氏志贺菌RNA的提取和反转录取Sf301按1:200接种于LB培养基,37 ℃振荡培养过夜,再按1:200转种于LB培养基培养6 h。收取菌液,离心,用含15 mg/mL溶菌酶的TE重悬菌体。采用RNeasy Mini Kit提取细菌RNA:加入RLT和无水乙醇裂解细菌,将裂解液转移至吸附柱进行离心吸附,用RW1和RPE洗脱,RNA-free水收集RNA。RNA在去除DNA(gDNA Eraser)后,反转录为cDNA(PrimeScript RT Enzyme Mix,37 ℃ 15 min,85 ℃ 5 s)。
1.2.3 福氏志贺菌rcsBDC操纵子共转录分析根据Sf301基因组中rcsB(2)、rcsC(3)、rcsD(4)的核苷酸序列及其上下游基因ompC(1)和SF2303(5)序列,在两两基因之间设计引物(表 1)。用细菌基因组DNA(genomic DNA,gDNA)提取试剂盒提取Sf301 gDNA。以cDNA为模板,RNA为阴性对照,gDNA为阳性对照,进行聚合酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction, PCR)扩增(2×Taq DNA聚合酶)。反应条件为:94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,59 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 2 min,30个循环;72 ℃ 10 min。
| Primers | Sequences (5′-3′) | Location | Product length (bp) |
| Co-transcriptional analysis by PCR | |||
| 12-F | CTACAGACTTGTCGTCAGAG | 2334002-2334021 | 1 097 |
| 12-R | ACGTAACGCCAGGTATCGAC | 2335098-2335079 | |
| 23-F | TCCATGCCAGCGGCTATTAT | 2337303-2337322 | 424 |
| 23-R | CATCCAGTTTCGGCAGGTTG | 2337726-2337707 | |
| 34-F | TTACGGTGACAAGCGTCTCT | 2338013-2338032 | 577 |
| 34-R | TGCCGGTAATCGGAGTAACT | 2338589-2338570 | |
| 45-F | CTGAGCCTGATCGGAACTCA | 2341099-2341118 | 627 |
| 45-R | GGCGCTATCAGGTGTATATC | 2341725-2341706 | |
| Transcription detection by qRT-PCR | |||
| rsmC-F | CTGCCCCGGCGGTAGAAGC | 4573886-4573868 | 126 |
| rsmC-R | ACGGCGGGTTGGAGATGAT | 4573761-4573779 | |
| rcsB-F | ATAGTCTTGTTCGGTATTCG | 2337618-2337637 | 83 |
| rcsB-R | AGTGCTGTAGAGTCTTCA | 2337700-2337683 | |
| rcsC-F | GCATCGTCGTTACAACATA | 2339090-2339072 | 76 |
| rcsC-R | TTACTCACTACCTCGTCAG | 2339015-2339033 | |
| rcsD-F | AAGTTGAAGAGGAAGAAG | 2336934-2336951 | 194 |
| rcsD-R | AGAGGCAGTAAGATTAGA | 2337127-2337110 | |
取过夜培养的Sf301按1:200转种于LB培养基,于不同时间点(4、5、6、8、10 h)收取菌液,按1.2.2提取RNA并反转录。以16S RNA基因rsmC为内参,根据Sf301的rcsB、rcsD、rcsC及rsmC核苷酸序列,用Beacon Designer 7设计引物(表 1),以cDNA为模板,用Eppendorf RealPlex 4(德国Eppendorf公司)进行qRT-RCR(SYBR Premix Ex Taq)。反应条件为:95 ℃ 2 min;95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 34 s,40个循环。计算3孔循环阈值(cycle threshold,Ct)的平均值,设生长4 h时所测基因和内参基因的Ct平均值分别为
配制不同pH值的LB培养基(pH 2.5、pH 3.5、pH 4.5、pH 5.0、pH 5.5、pH 6.5、pH 7.5),以及不同渗透压的LB培养基(NaCl浓度分别为0.05、0.1、0.2、0.4、0.8、1.2、1.6、2.0 mol/L)。取上述LB培养基各200 μL加入96孔板,每3孔重复加1种培养基。取过夜培养的Sf301按1:200转种于各培养基,用全自动生长曲线分析仪(Bioscreen,芬兰)测定OD600,每0.5 h测1次,连续测24 h。用GraphPad Prism 5制作生长曲线。
1.2.6 酸性和渗透压条件下福氏志贺菌rcsB、rcsD、rcsC的转录水平分析取过夜培养的Sf301按1:200转种于正常LB培养基,pH 5.5和pH 6.5的酸性LB培养基,以及NaCl浓度为0.4和0.8 mol/L的高渗LB培养基,于6 h和10 h收取菌液,按1.2.2提取RNA并反转录,按1.2.4进行qRT-RCR。设正常LB培养基培养时所测基因和内参基因的Ct平均值为
使用Graphpad Prism 5软件进行统计学分析。在不同培养时间点的基因转录水平分析中,采用Two-way ANOVA双因素方差分析,统计学结果选取以时间点为因素的统计量F值和P值。在不同pH值和渗透压条件下的基因转录水平分析中,采用Two-way ANOVA双因素方差分析结合Bonferroni post hoc test多重检验方法,统计学结果选取各压力条件和正常条件下基因转录水平两两比较的P值。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
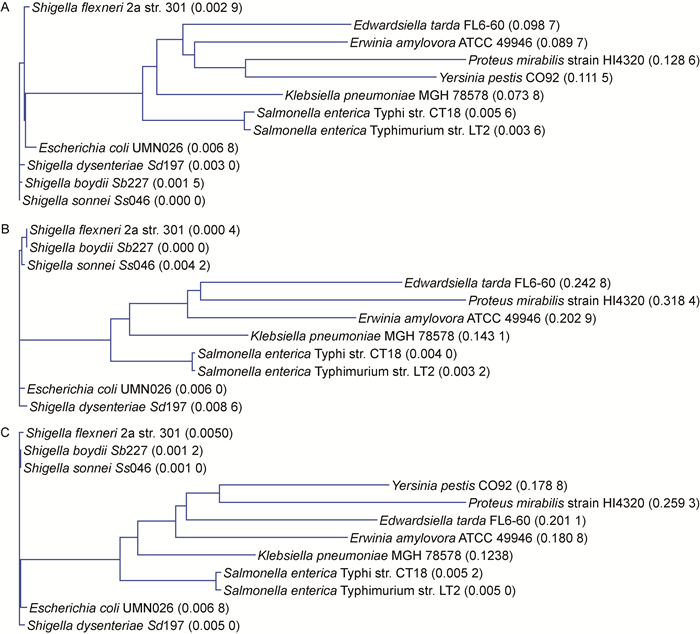
2 结果 2.1 福氏志贺菌rcsBDC基因簇的生物信息学分析为研究福氏志贺菌rcsBDC基因簇的同源性和蛋白结构域,进行生物信息学分析。通过比对Sf301与其他细菌rcsB、rcsC、rcsD核苷酸序列的相似性,发现Sf301与其他亚群志贺菌(Ss046、Sb227、Sd197)相比,rcsB、rcsD、rcsC序列的同源性分别为99.1%~99.4%、98.0%~100.0%、98.9%~99.2%。Sf301与大肠埃希菌UMN026的rcsB、rcsC、rcsD同源性均高达98.4%以上。Sf301与肠杆菌科其他细菌相比,rcsB、rcsD、rcsC的同源性分别为(80.90±4.68)%、(64.03±12.96)%、(66.90±9.52)%(表 2)。进化树分析显示,Sf301与其他亚群志贺菌及大肠埃希菌在进化上距离最近,与沙门菌亲缘性次之,而与肠杆菌科其他细菌相对较远(图 1)。
| Strains | rcsB | rcsD | rcsC | |||||
| Length (nt) |
Identity (%) |
Length (nt) |
Identity (%) |
Length (nt) |
Identity (%) |
|||
| Shigella sonnei Ss046 | 651 | 99.4 | 2 673 | 98.9 | 2 850 | 99.2 | ||
| Shigella boydii Sb227 | 651 | 99.2 | 2 673 | 100.0 | 2 850 | 99.2 | ||
| Shigella dysenteriae Sd197 | 651 | 99.1 | 2 673 | 98.0 | 2 850 | 98.9 | ||
| Escherichia coli UMN026 | 651 | 98.9 | 2 673 | 98.4 | 2 850 | 98.6 | ||
| Salmonella enterica Typhimurium LT2 | 666 | 84.7 | 2 686 | 77.3 | 2 847 | 77.7 | ||
| Salmonella enterica Typhi CT18 | 651 | 86.3 | 2 670 | 77.7 | 2 847 | 77.6 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae MGH 78578 | 651 | 84.5 | 2 658 | 70.8 | 2 841 | 74.3 | ||
| Erwinia amylovora ATCC 49946 | 648 | 80.0 | 2 658 | 57.7 | 2 964 | 62.2 | ||
| Edwardsiella tarda FL6-60 | 654 | 80.8 | 2 697 | 53.2 | 2 871 | 61.9 | ||
| Yersinia pestis CO92 | 654 | 76.5 | Not found | Not found | 2 874 | 60.9 | ||
| Proteus mirabilis HI4320 | 657 | 73.5 | 2 694 | 47.5 | 2 829 | 53.7 | ||
| Gene rcsD was not found in the genome of Yersinia pestis CO92. nt: nucleotide. | ||||||||
|
| A: rcsB. B: rcsD. C: rcsC. 图 1 肠杆菌科细菌rcsB、rcsD、rcsC进化树 Fig. 1 Phylogenetic trees of rcsB, rcsD and rcsC in Enterobacteriacea |
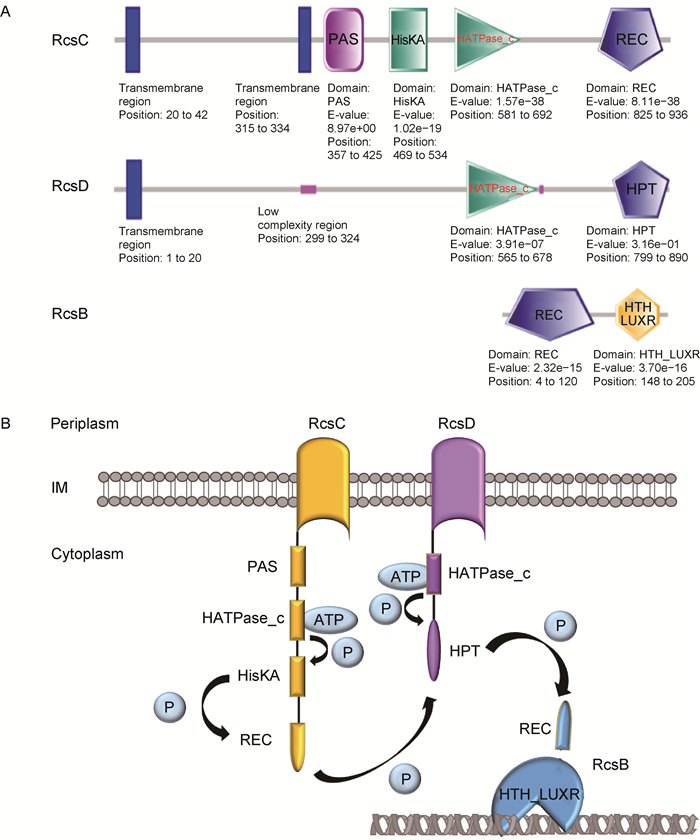
利用SMART数据库,根据Sf301的RcsB、RcsD、RcsC氨基酸序列预测蛋白结构域,发现RcsC含2个跨膜区和PAS(Per-Arnt-Sim)、HisKA(histidine kinase)、HATPase_c(histidine kinase/HSP90-like ATPase)、REC(receiver)域; RcsD含1个跨膜区和HPT(histidine phosphotransferase)、HATPase_c域; RcsB含REC和HTH_LUXR(LuxR-type DNA binding helix-turn-helix)域(图 2A)。
|
| A: The domains were predicted by SMART database according to the amino acid sequences of RcsC, RcsD, RcsB in Sf301. B: The phosphotransfer among the domains of RcsBDC was inferred from references[6, 16-17]. Upon PAS sensing signals, HisHA undergoes autophosphorylation of the histidine with ATP under the catalysis of HATPase_c domain, and transfers the phosphate group to the aspartate on REC. The phosphate group is then transferred to histidine on HPT and further to aspartate on the terminal REC of RR (His-Asp-His-Asp). After activation by phosphorylation of REC, HTH_LUXR binds DNA in the major groove and works as a transcriptional regulator. 图 2 福氏志贺菌RcsC、RcsD、RcsB蛋白结构域 Fig. 2 The domains of RcsC, RcsD and RcsB in Shigella flexneri |
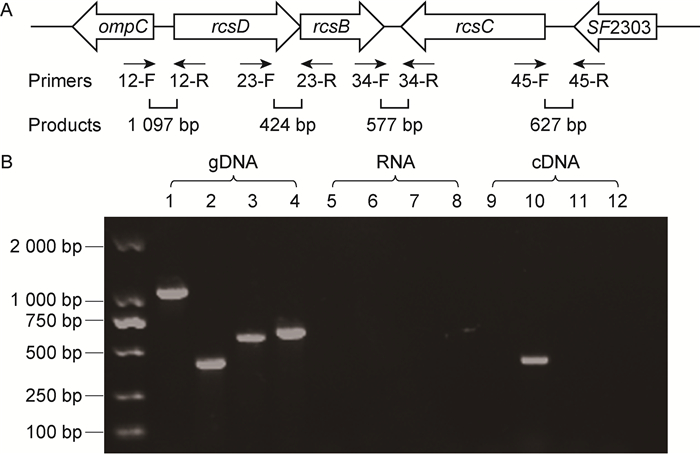
为研究福氏志贺菌Sf301的rcsB、rcsD、rcsC之间及其与上下游基因之间是否存在共转录,设计4对引物(图 3A),以Sf301 cDNA为模板进行PCR,gDNA为对照。结果显示,以gDNA为模板可扩增出1 097 bp(12-F/12-R)、424 bp(23-F/23-R)、577 bp(34-F/34-R)和627 bp(45-F/45-R)的片段,而以cDNA为模板仅扩增出424 bp(23-F/23-R)片段(图 3B)。提示在Sf301中,rcsB和rcsD处于同一条mRNA链,rcsB与rcsC之间及rcsBDC与上下游基因之间均不存在共转录。
|
| A: The primers 12-F/12-R, 23-F/23-R, 34-F/34-R, 45-F/45-R were designed. B: Genomic DNA (gDNA), RNA and cDNA of Sf301 were used as templets. Primers 12-F/12-R were used in columns 1/5/9, 23-F/23-R in columns 2/6/10, 34-F/34-R in columns 3/7/11, and 45-F/45-R in columns 4/8/12. 图 3 福氏志贺菌Sf301的rcsBDC操纵子共转录分析 Fig. 3 Co-transcriptional analysis of rcsBDC operon in Sf301 |
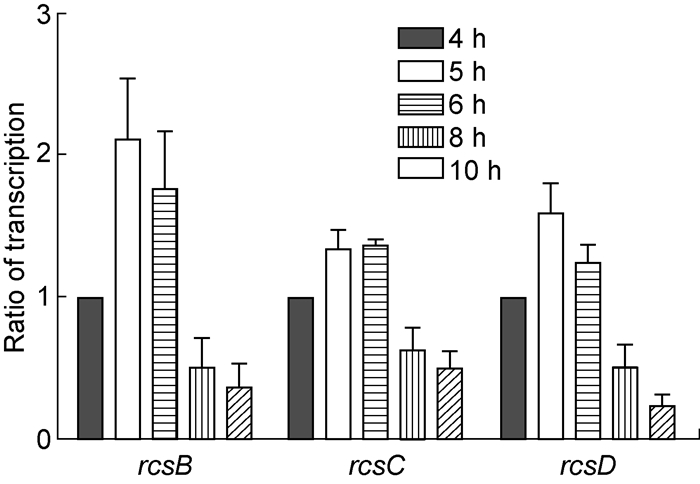
为分析福氏志贺菌不同生长时间点的rcsB、rcsD、rcsC表达水平,分别提取Sf301生长4、5、6、8和10 h的RNA,通过qRT-PCR检测rcsB、rcsC、rcsD转录水平。结果显示,rcsB、rcsD基因转录水平在生长5 h(对数中期)时达高峰,6 h后逐渐下降;rcsC基因转录水平在生长6 h时达高峰,8 h后(对数晚期)逐渐下降(F=23.97,P<0.001)(图 4)。
|
| Overnight cultures were inoculated at 1:200 into LB and harvested at 4 h, 5 h, 6 h, 8 h and 10 h of growth. Their total RNAs were isolated and reversely transcribed into cDNAs, which were used as templets. The transcriptional levels of rcsB, rcsC and rcsD were analyzed by qRT-PCR. 图 4 福氏志贺菌rcsB、rcsC、rcsD不同时间点的转录水平 Fig. 4 Transcriptional levels of rcsB, rcsC and rcsD at different time points in Shigella flexneri |
为研究酸性环境对福氏志贺菌rcsB、rcsD、rcsC转录水平的影响,首先检测不同pH条件下Sf301的生长曲线。结果显示,Sf301在pH 6.5条件下的生长曲线与pH 7.5时一致,于2 h进入对数期,8 h进入稳定期;在pH 5.5条件下,细菌生长明显变慢,于4 h进入对数期,10 h进入稳定期,其稳定期的OD600稍高于pH 6.5和pH 7.5条件下的稳定期;在pH 5.0及以下的酸性环境中,细菌的生长基本停滞(图 5A)。
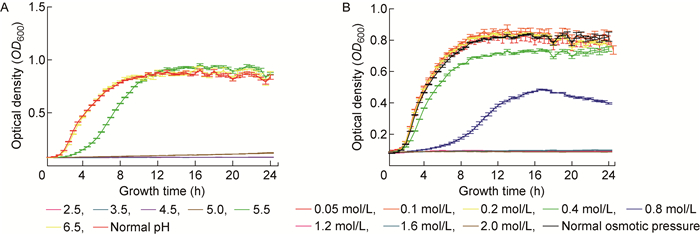
|
| The growth curves of Shigella flexneri under different pH (A) and osmotic pressure (B). Overnight cultures were inoculated at 1:200 into LB under different conditions. The OD600 was tested every half an hour. Three replications were tested for each strain grown under each condition to obtain mean and standard deviation. 图 5 福氏志贺菌在环境压力中的生长曲线 Fig. 5 The growth curves of Shigella flexneri under environmental stresses |
进一步选取对数中期(6 h)和稳定期(10 h)两个时间点,检测Sf301在酸性培养条件下rcsB、rcsD、rcsC的转录水平。结果显示,当细菌在pH 6.5或pH 5.5条件下培养6 h时,rcsB、rcsC、rcsD转录水平无明显改变(图 6A)。在pH 6.5或pH 5.5条件下培养10 h时,细菌rcsB转录水平明显高于pH 7.5条件〔(4.30±0.96)倍,P<0.05;(5.64±1.18)倍,P<0.001〕,rcsD转录水平也明显升高〔(3.83±0.77)倍,P<0.05;(4.82±1.30)倍,P<0.01〕。rcsC转录水平在pH 6.5、pH 5.5及pH 7.5条件下无明显差异(P>0.05)(图 6B)。
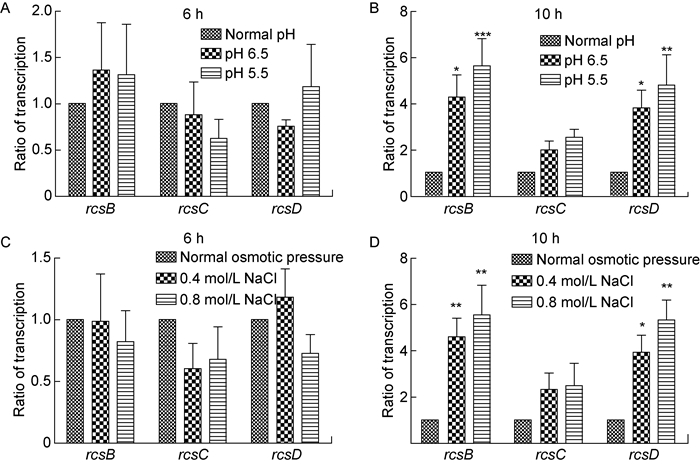
|
| Overnight cultures were inoculated at 1:200 into LB under normal condition, pH 6.5, pH 5.5, 0.4 mol/L NaCl and 0.8 mol/L NaCl, and were harvested at 6 h and 10 h. Total RNAs were extracted and reversely transcribed into cDNAs. The transcriptional levels of rcsB, rcsD and rcsC were detected by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. 图 6 环境压力对福氏志贺菌rcsB、rcsD、rcsC转录水平的影响 Fig. 6 The effect of environmental stresses on transcriptional levels of rcsB, rcsD, rcsC in Shigella flexneri |
为研究渗透压对福氏志贺菌rcsB、rcsD、rcsC转录的影响,首先测定Sf301在不同渗透压下的生长曲线。结果显示,Sf301在0.2 mol/L NaCl及以下渗透压中的生长曲线与正常渗透压中一致,于2 h进入对数期,8 h进入稳定期;在0.8 mol/L NaCl渗透压中生长明显变慢,于6 h进入对数期,14 h进入稳定期,且其在对数期和稳定期的OD600明显低于正常值;在1.2 mol/L NaCl及以上渗透压中,志贺菌生长停滞(图 5B)。
进一步选取对数中期(6 h)和稳定期(10 h)两个时间点,检测Sf301在高渗培养条件下rcsB、rcsD、rcsC的转录水平。结果显示,细菌在0.4 mol/L或0.8 mol/L NaCl渗透压中培养6 h时,rcsB、rcsC、rcsD转录水平无明显改变(图 6C)。在0.4 mol/L或0.8 mol/L NaCl渗透压中培养10 h时,细菌rcsB转录水平明显高于正常渗透压〔(4.60±0.81)倍,P<0.01;(5.55±1.28)倍,P<0.01〕,rcsD的转录水平也明显升高〔(3.94±0.74)倍,P<0.05;(5.34±0.86)倍,P<0.01〕。rcsC转录水平在0.4 mol/L、0.8 mol/L NaCl及正常渗透压中无明显差异(P>0.05)(图 6D)。
3 讨论大肠埃希菌中,Rcs调控细菌的抗酸性和生物膜形成等生物学特性[5]。志贺菌与大肠埃希菌的亲缘性非常近,又进化出特定的致病性和生理特性[15]。因此,分析志贺菌的Rcs系统对其分子致病机制研究具有重要意义。通过生物信息学分析发现,福氏志贺菌的rcsBDC除与其他亚群志贺菌高度同源外,与大肠埃希菌和沙门菌也有较高的同源性。在进化树上,志贺菌中rcsBDC与大肠埃希菌最为靠近,沙门菌次之,提示志贺菌Rcs系统可能与大肠埃希菌和沙门菌一样,对细菌生物学功能具有重要调控作用。
Rcs系统主要含RcsB、RcsC、RcsD 3个组分,各组分的结构和功能较典型TCS更为复杂。分析福氏志贺菌RcsB、RcsC、RcsD的结构域,结合文献报道,推测当RcsC-PAS感受信号后,HATPase_c催化ATP水解产生磷酸基团,将HisKA的His磷酸化(此过程称自磷酸化),继而磷酸转移至REC域的Asp[16]。RcsC-REC将磷酸传递给RcsD-HPT,使His磷酸化后又转移至Asp[17]。此外,RcsD含HATPase_c,提示RcsD可能在信号刺激下自磷酸化,形成不依赖RcsC的信号转导通路[6]。RcsB-REC接受来自RcsD的磷酸基团激活HTH_LUXR,后者结合下游基因启动子区域DNA而调控靶基因表达(图 2B)。因此,福氏志贺菌Sf301的RcsBDC蛋白具备完整的TCS功能域,可通过磷酸转移机制实现信号转导。
在鼠伤寒沙门菌中,rcsB基因由PrcsDB和PrcsB两个启动子启动转录,其中PrcsDB为rcsD与rcsB共同启动子[18-19]。在福氏志贺菌Sf301基因组中,rcsD位于rcsB上游,与rcsB同向,两者仅相距17 bp;rcsC位于rcsB下游,与rcsB反向且相距200 bp。本研究对rcsBDC及其上下游基因的cDNA进行PCR分析,发现rcsD与rcsB之间存在共转录,提示福氏志贺菌与鼠伤寒沙门菌一样,rcsD与rcsB具有共同的启动子。
志贺菌在感染过程必须经过胃肠道中的酸性、渗透压环境,因此分析外环境对志贺菌Rcs系统的影响对其致病性研究具有重要意义。大肠埃希菌中,酸性、渗透压、葡萄糖、锌离子和低温环境等均可激活Rcs系统,从而影响其下游基因表达[20-22],但外环境压力对rcsB、rcsD、rcsC基因转录水平的影响尚未见报道。本研究发现,在福氏志贺菌对数生长中期(6 h),酸性、高渗条件对rcsB、rcsD、rcsC的转录水平均无明显影响,这可能是由于rcsB、rcsD、rcsC在生长6 h时的转录水平较高,已能满足其发挥功能所需的表达量;而在rcsB、rcsD、rcsC转录水平较低的稳定期(10 h),酸性、渗透压条件下rcsB和rcsD的转录水平显著高于正常条件,提示外环境压力使福氏志贺菌生长稳定期的rcsB、rcsD基因转录水平上调。此外,本研究还检测了多黏菌素B条件下rcsB、rcsD、rcsC的转录水平,未发现明显变化。
综上所述,本研究初步探索了外环境对福氏志贺菌rcsB、rcsD、rcsC基因转录的影响,发现酸性和高渗透压环境可促进rcsB和rcsD基因转录,为志贺菌Rcs系统的功能机制研究提供了一定理论基础。
| [1] |
Wuichet K, Cantwell BJ, Zhulin IB. Evolution and phyletic distribution of two-component signal transduction systems[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2010, 13(2): 219-225.
[DOI]
|
| [2] |
Galperin MY, Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Koonin EV. Phyletic distribution and lineage-specific domain architectures of archaeal two-component signal transduction systems[J]. J Bacteriol, 2018.
[DOI]
|
| [3] |
Casino P, Rubio V, Marina A. The mechanism of signal transduction by two-component systems[J]. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 2010, 20(6): 763-771.
[DOI]
|
| [4] |
陈嘉瑜, 蔡霞, 瞿涤. 沙门菌PhoP-PhoQ双组分信号转导系统[J]. 微生物与感染, 2010, 5(4): 239-242. [URI]
|
| [5] |
Pannen D, Fabisch M, Gausling L, Schnetz K. Interaction of the RcsB response regulator with auxiliary transcription regulators in Escherichia coli[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(5): 2357-2370.
[DOI]
|
| [6] |
Pescaretti ML, Farizano JV, Morero R, Delgado MA. A novel insight on signal transduction mechanism of RcsCDB system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e72527.
[DOI]
|
| [7] |
Llobet E, Campos MA, Gimenez P, Moranta D, Bengoechea JA. Analysis of the networks controlling the antimicrobial-peptide-dependent induction of Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence factors[J]. Infect Immun, 2011, 79(9): 3718-3732.
[DOI]
|
| [8] |
Howery KE, Clemmer KM, Rather PN. The Rcs regulon in Proteus mirabilis: implications for motility, biofilm formation, and virulence[J]. Curr Genet, 2016, 62(4): 775-789.
[DOI]
|
| [9] |
Li Y, Hu Y, Francis MS, Chen S. RcsB positively regulates the Yersinia Ysc-Yop type Ⅲ secretion system by activating expression of the master transcriptional regulator LcrF[J]. Environ Microbiol, 2015, 17(4): 1219-1233.
[DOI]
|
| [10] |
Ancona V, Chatnaparat T, Zhao Y. Conserved aspartate and lysine residues of RcsB are required for amylovoran biosynthesis, virulence, and DNA binding in Erwinia amylovora[J]. Mol Genet Genomics, 2015, 290(4): 1265-1276.
[DOI]
|
| [11] |
Xu Y, Xu T, Wang B, Dong X, Sheng A, Zhang XH. A mutation in rcsB, a gene encoding the core component of the Rcs cascade, enhances the virulence of Edwardsiella tarda[J]. Res Microbiol, 2014, 165(3): 226-232.
[DOI]
|
| [12] |
Livio S, Strockbine NA, Panchalingam S, Tennant SM, Barry EM, Marohn ME, Antonio M, Hossain A, Mandomando I, Ochieng JB, Oundo JO, Qureshi S, Ramamurthy T, Tamboura B, Adegbola RA, Hossain MJ, Saha D, Sen S, Faruque AS, Alonso PL, Breiman RF, Zaidi AK, Sur D, Sow SO, Berkeley LY, O'Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Biswas K, Cohen D, Farag TH, Nasrin D, Wu Y, Blackwelder WC, Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Levine MM. Shigella isolates from the global enteric multicenter study inform vaccine development[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2014, 59(7): 933-941.
[DOI]
|
| [13] |
Marteyn B, Gazi A, Sansonetti P. Shigella: a model of virulence regulation in vivo[J]. Gut Microbes, 2012, 3(2): 104-120.
[DOI]
|
| [14] |
王传清, 何磊艳, 王爱敏, 张文宏. 2007年上海市儿童社区获得性腹泻致病菌谱分析[J]. 微生物与感染, 2009, 4(2): 97-100. [URI]
|
| [15] |
Ud-Din A, Wahid S. Relationship among Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) and their differentiation[J]. Braz J Microbiol, 2014, 45(4): 1131-1138.
[DOI]
|
| [16] |
Vierstra RD, Davis SJ. Bacteriophytochromes: new tools for understanding phytochrome signal transduction[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2000, 11(6): 511-521.
[DOI]
|
| [17] |
Janiak-Spens F, Sparling DP, West AH. Novel role for an HPt domain in stabilizing the phosphorylated state of a response regulator domain[J]. J Bacteriol, 2000, 182(23): 6673-6678.
[DOI]
|
| [18] |
Pescaretti ML, Lopez FE, Morero RD, Delgado MA. Transcriptional autoregulation of the RcsCDB phosphorelay system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium[J]. Microbiology, 2010, 156(Pt 12): 3513-3521.
[PMC]
|
| [19] |
Pescaretti ML, Morero R, Delgado MA. Identification of a new promoter for the response regulator rcsB expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium[J]. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2009, 300(2): 165-173.
[DOI]
|
| [20] |
Sledjeski DD, Gottesman S. Osmotic shock induction of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12[J]. J Bacteriol, 1996, 178(4): 1204-1206.
[DOI]
|
| [21] |
Kannan G, Wilks JC, Fitzgerald DM, Jones BD, Bondurant SS, Slonczewski JL. Rapid acid treatment of Escherichia coli: transcriptomic response and recovery[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2008, 8: 37.
[DOI]
|
| [22] |
Hagiwara D, Sugiura M, Oshima T, Mori H, Aiba H, Yamashino T, Mizuno T. Genome-wide analyses revealing a signaling network of the RcsC-YojN-RcsB phosphorelay system in Escherichia coli[J]. J Bacteriol, 2003, 185(19): 5735-5746.
[DOI]
|
 2018, Vol. 13
2018, Vol. 13


